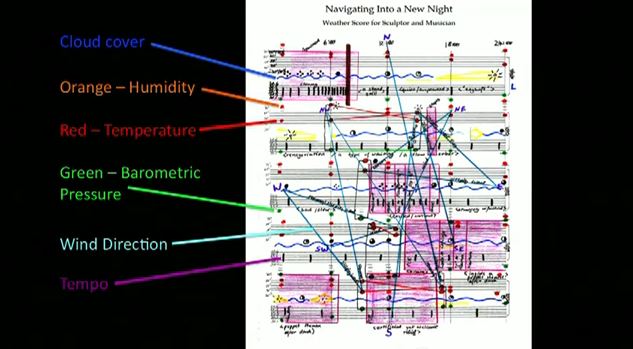
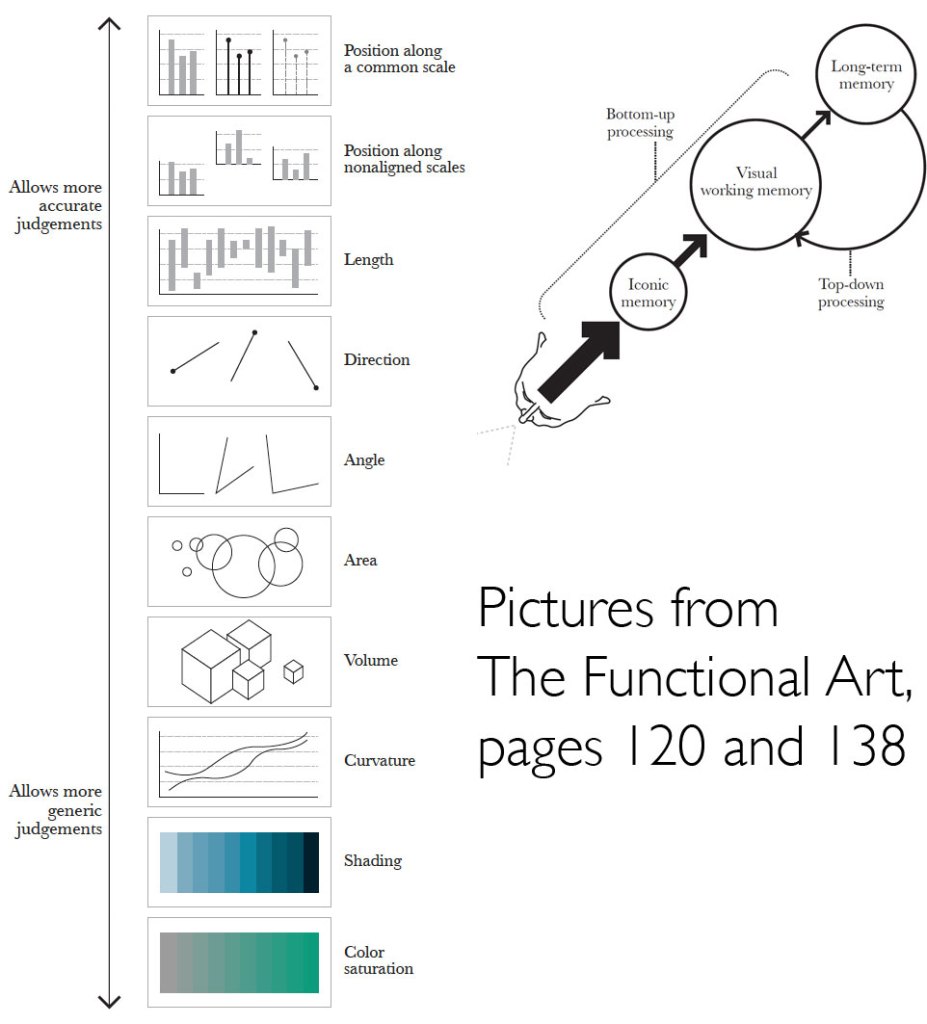
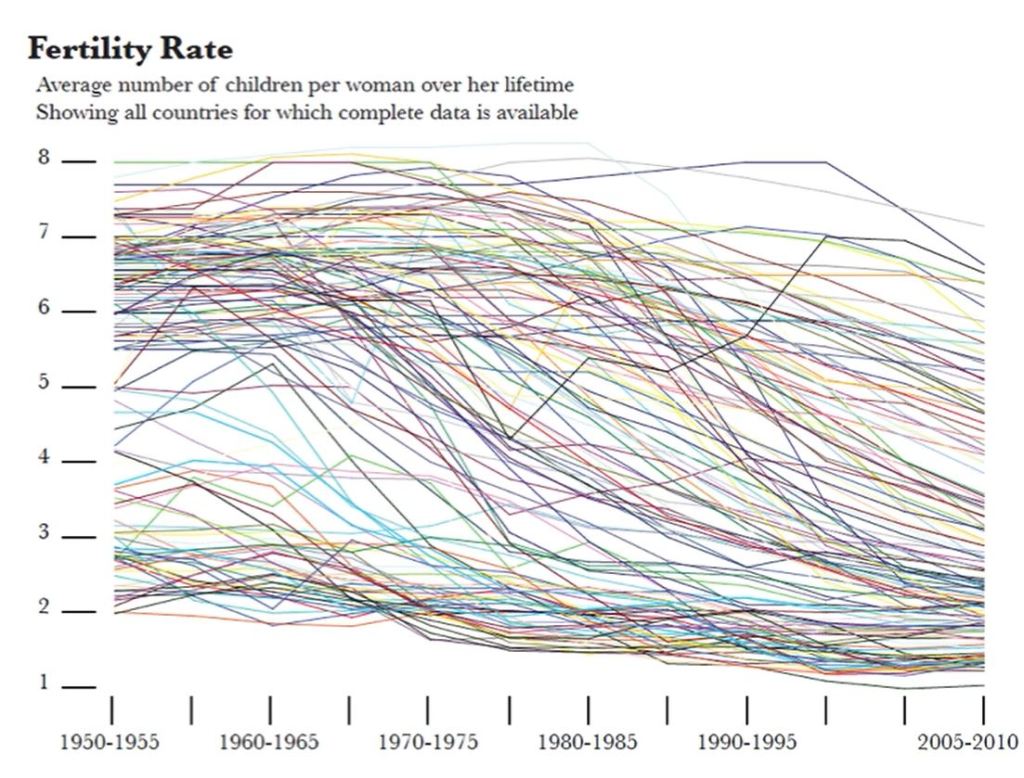
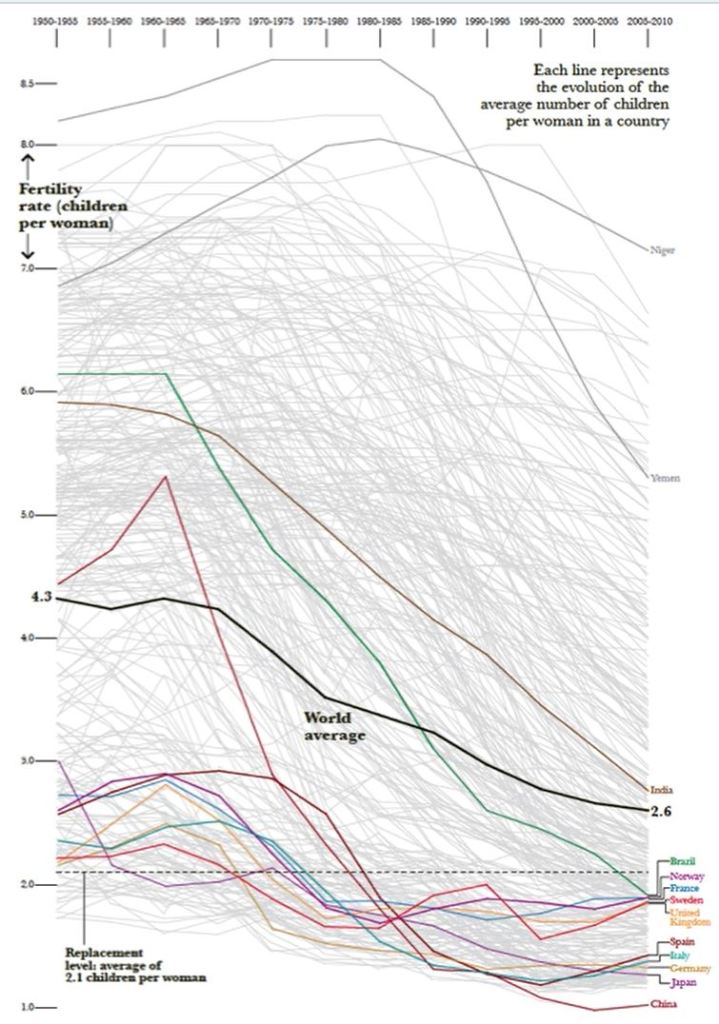
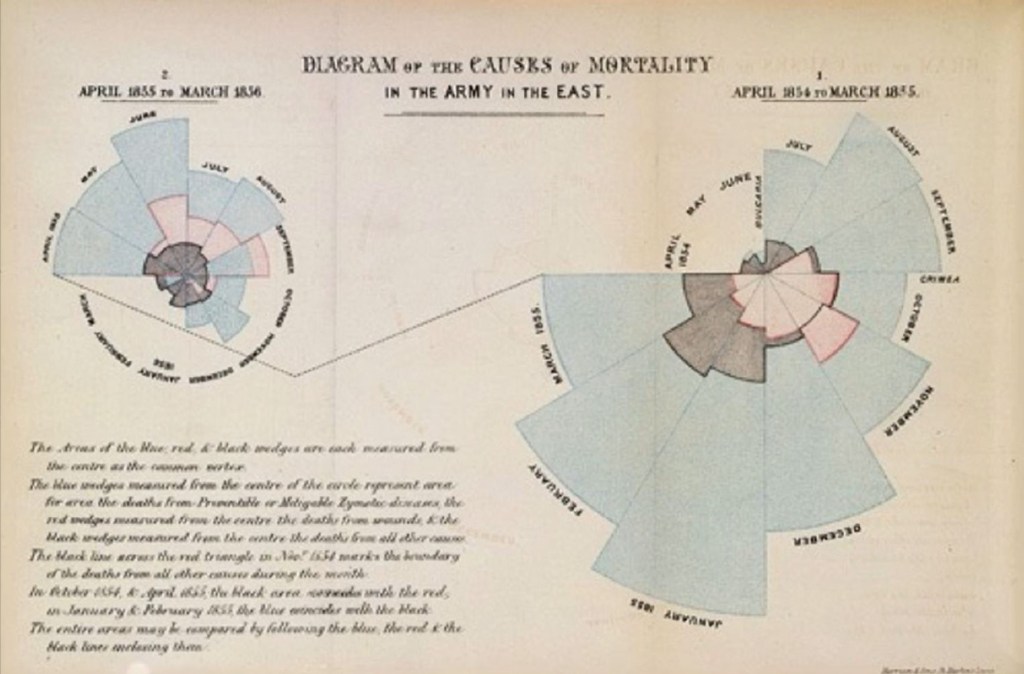
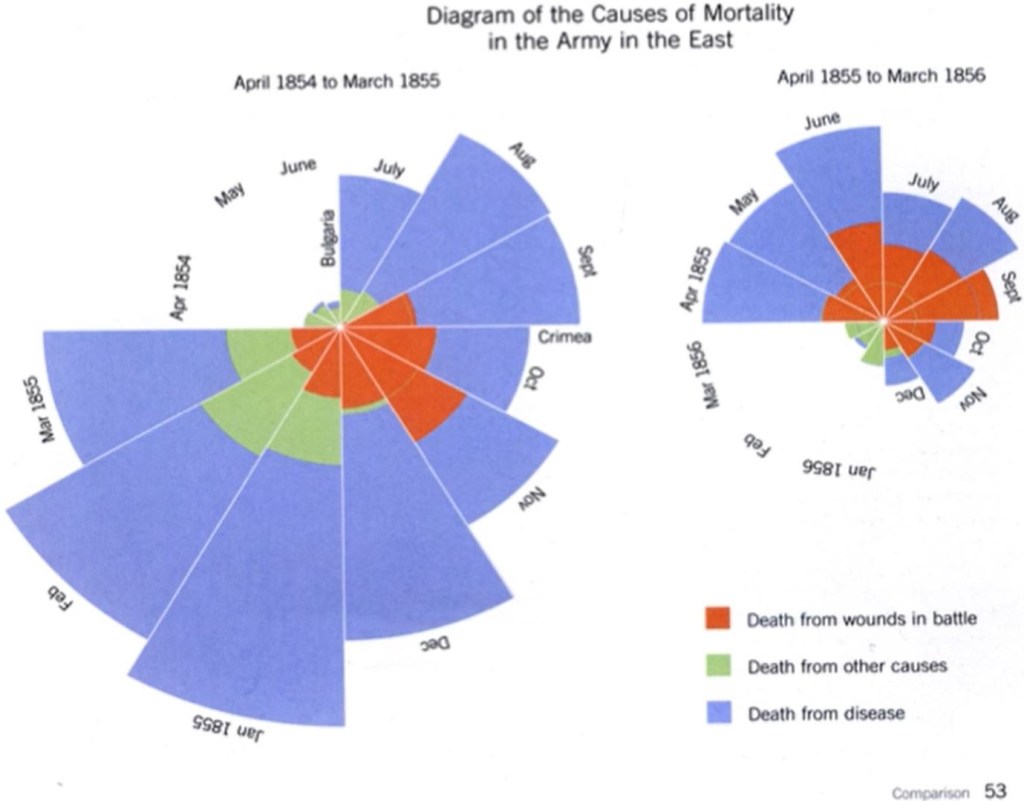
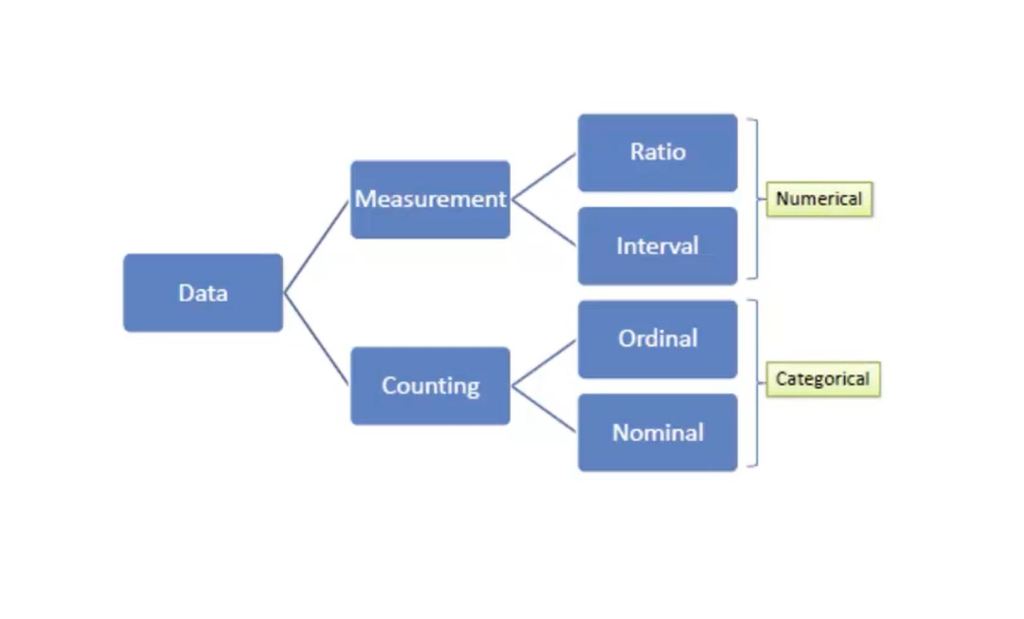
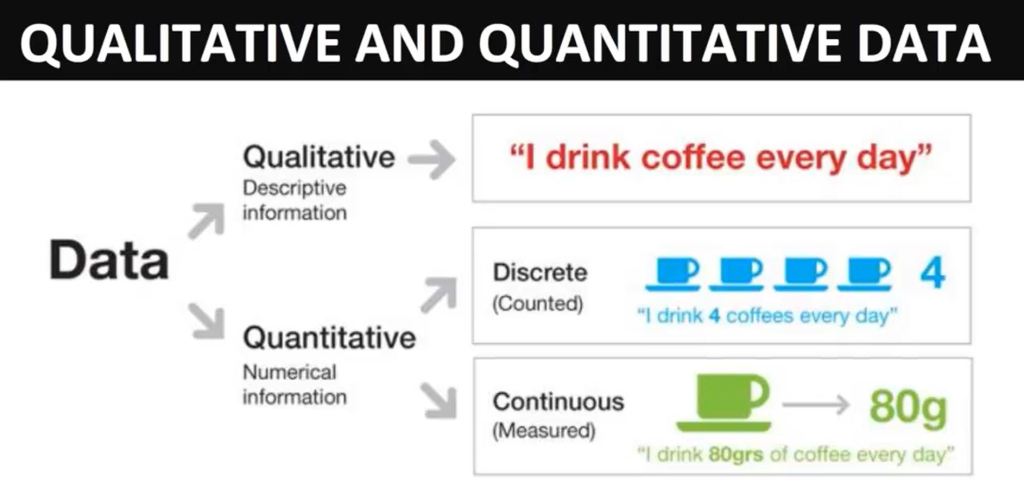
What is data?
- Data is a measurement.
- Data are values of qualitive or quantitative variables belonging to a set of items.
- Data are typically the results of measurements and can be visualised using graphs or images.
- The terms data, information and knowledge are frequently used for overlapping concepts.
- Data by itself carries no meaning; for data to become information it must be interpreted and take on a meaning.
What is data visualisation?
- Data visualisation is the visualisation of data.
- Data visualisation is viewed by many disciplines as a modern equivalent of visual communication.
- It involves the creation and study of the visual representation of data. This is further explained through the words of Michael Friendly (2008) as,
“information that has been abstracted in some schematic form, including attributes or variables for the units of information”.
- Data visualisation is one of the steps in analysing data and presenting it to users.
- The primary goal of visualisation is to communicate information clearly and efficiently using statistical graphics, plots and information graphics.
Information graphics v data visualisation
- Not all information visualisations are based on data, but all data visualisations are information visualisations.
- Infographics are not based on data.
- Effective visualisations help users analyse and reason about data and evidence.
- Visualisations make complex data more accessible along with easy to understand and use.
- Data visualisation is both an art and a science.
- The focus of data visualisation is choosing the right visualisation type for different data sets. As well as wrangling data which is organising data so it can be used in our visualisations.
- Wrangling data is the of process cleaning and unifying complex data sets for analysis to create ease in transforming and mapping data sets into visualisations that has an intended purpose.
Types of data visualisations
- Bar chart – best used for communicating two variables
- Line chart – best used for data over time
- In using a basic chart your audience knows them well, which means they can be immediately recognised by them, they know how to read them and they won’t be confused by them.
- We need to ensure we understand our audience and how they read images and take this in account when designing visualisations.
Reflection
Data visualisation is the graphical representation of information and data. It is another form of visual art that is aimed to convey useful information in an engaging way. A chart enables us to quickly see trends and outliers. If we can see something, we interpret it quickly. Data visualisation is storytelling with a purpose. A spreadsheet of data can be hard to process and can be overwhelming to look at. Data visualisations are a much more effective and intuitive way to convey information.